composable tutorials
personalized documentation experiences
Disclaimer: Certain details, processes, and data have been omitted from this case study due to a non-disclosure agreement (NDA). For a more comprehensive view of my work and design process, please contact me directly.
good to know terms
documentation components
reusable content blocks that docs writers can use to build pages. think of them like lego pieces that can be combined in different ways to create customized user experiences.
nested tabs
tabs within tabs, creating complex navigation structures. while functional, they create poor user experiences and are difficult for AI systems to parse and understand.
content permutations
different combinations of content based on user choices. for example, instructions might vary based on programming language, deployment method, and database version.
llm optimization
designing content structure so that large language models (like chatgpt) can better understand and reference documentation when helping users.
project overview
the challenge
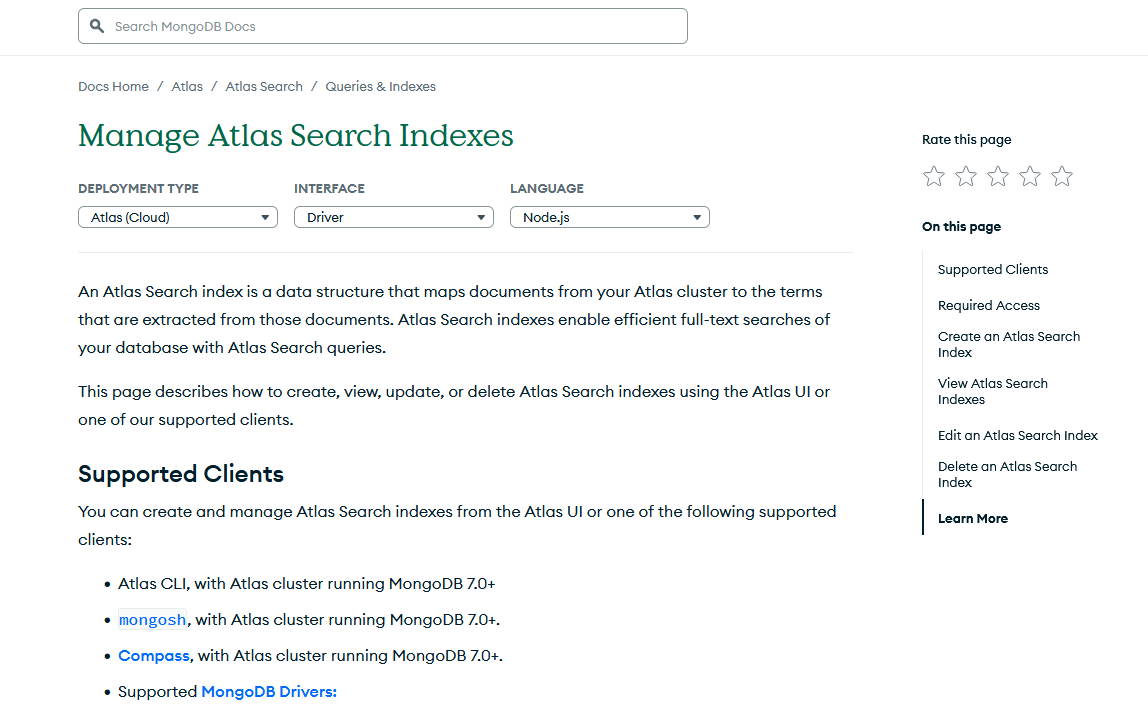
mongodb documentation pages often need to serve multiple user contexts - different programming languages, deployment methods, database versions, and experience levels. traditional approaches using nested tabs created confusing navigation and forced users to make repeated selections throughout their reading experience.
the solution
i designed a composable tutorial system that allows users to customize their documentation experience upfront. by making key selections at the beginning of their journey, users receive a personalized, linear reading experience tailored to their specific context and needs.
the impact
the composable tutorial system eliminated nested tabs, improved content discoverability, and created better experiences for both human readers and ai systems. it also empowered docs writers with a flexible authoring system that scales with content complexity.
the dual user challenge
this project presented a unique design challenge: optimizing for two distinct user groups with different needs and workflows.
external users
docs writers
the design constraint
any solution needed to be enthusiastically adopted by docs writers, as they would be the ones implementing and maintaining the system. this meant the authoring experience was just as critical as the reading experience - if writers found the system cumbersome, it would fail regardless of how well it served end users.
understanding the problem
the nested tabs nightmare
before the composable tutorial system, complex documentation pages relied heavily on nested tabs to manage content variations:
user experience issues:
- • users lost context when switching between nested tabs
- • repeated selection fatigue throughout reading
- • difficult to bookmark or share specific configurations
- • mobile experience was particularly poor
technical limitations:
- • llms struggled to parse nested content structures
- • search engines couldn't index content effectively
- • analytics couldn't track user paths accurately
- • accessibility issues with complex tab navigation
content complexity explosion
as mongodb's product ecosystem grew, documentation pages needed to accommodate an increasing number of variables:
with 4-5 variables each having 3-8 options, some pages theoretically needed to support hundreds of content permutations.
impact & adoption
business & technical impact
key learnings
design for your content creators
the most important insight from this project was that content systems succeed or fail based on creator adoption. no matter how well a system serves end users, if the people creating content find it difficult or cumbersome, it won't be used. investing heavily in the authoring experience was crucial to the project's success.
upfront choices create better experiences
users strongly preferred making their customization choices at the beginning of their journey rather than throughout their reading experience. this "configuration first" approach eliminated context switching and created more focused, linear experiences that felt tailored to their specific needs.
design for the future of content consumption
optimizing for ai systems and search engines wasn't just a nice-to-have - it became essential as more users discover and consume documentation through ai assistants. designing content structure that works well for both human readers and machine parsing creates more resilient, future-proof documentation systems.
the composable tutorial system demonstrates how thoughtful component design can solve complex content challenges while empowering both creators and consumers.